Chmod permission using –reference can copy the permission from one file to another file in Linux using –reference command Basic Syntax chmod –reference ref_file target_file Example Let us take two files, file 1 having all readwriteexecute permission and another file 2 having only read permission for owner, group and otherThis command will do the trick chmod u=rwx,g=rx,o=r myfile This example uses symbolicThe chmod command A normal consequence of applying strict file permissions, and sometimes a nuisance, is that access rights will need to be changed for all kinds of reasons We use the chmod command to do this, and eventually to chmod has become an almost acceptable English verb, meaning the changing of the access mode of a file

How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux The Wise Bulb
Chmod command in linux with options and examples
Chmod command in linux with options and examples-Remove execute permission to others in file chmod gor ;The chmod command is used in Linux (and Unixlike systems) to set the permissions of files and directories First of all, here is the generic syntax of the chmod command chmod The permission part of the command can have different formats



Top 50 Linux Commands Command Line Interface Computer File
This tutorial explains chmod command symbolic notation (r, w, x, a) and octal notation (0, 1, 2, 4) in detail with chmod command arguments and options Learn how chmod command is used to manage Linux permission levels (user, group and other) and types (read, write and execute) step by step with practical examplesUsing "Chmod x" Command on Linux and Unix with Examples In Linux systems, " chmod " command is used to determine the access rights of users to files It allows us to change the access permissions of the files we specify The exact equivalent of chmod is change modeThe example below uses alphanumeric options in order to solve a problem that commonly occurs with
Using "Chmod x" Command on Linux and Unix with Examples In Linux systems, " chmod " command is used to determine the access rights of users to files It allows us to change the access permissions of the files we specify The exact equivalent of chmod is change modeLet's now delve and see different examples of chmod command Example 1) Assign permissions using numeric notation When setting permissions using the numeric style/notation, use the syntax shown below $ sudo chmod OPTIONS numeric_value filename The numeric value can take 3 or 4 numbers However, in most cases, 3 numbers are usedExamples chmod ugx file ;
Reference File Setuid Setgid Sticky Bit Use the octal CHMOD Command chmod R 700 folder_name OR use the symbolic CHMOD Command chmod R arwx,grwx,orwx folder_nameRemove the execute permission for all users chmod ax filename;Chmod command is used to change access permission of files and directories in Linux operating systemschmod stands for change modeAccess permissions specify whether a user account or group can read, write, or execute a given file and directory chmod Command Syntax



Understand Linux System File Permission



Chmod File Permissions In Linux Unix Linux Angular Angular Js Jquery Php Mysql And Web Development Tutorials
Linux (X) commonly used commands Rights Management Command the command chmod permissions management Front once said that everything in the form of files in Linux So this command is to modify file permissions for Only two types of users can use this command 1We want the user dave to have read and write permissions and the group and other users to have read permissions only We can do using the following command chmod u=rw,og=r new_filetxt Using the "=" operator means we wipe out any existing permissions and then set the ones specified let's check the new permission on this file ls l new_filetxtMoving on, if you want, you can also simply copy permissions granted to, say, the owner/current user and have them for the group or others For this use the sign '=' For example, to copy owner/user permissions to group, use the following command chmod g=u scriptsh



Command Line Quick Tips More About Permissions Fedora Magazine



Linux Commands Linuxconfig Org
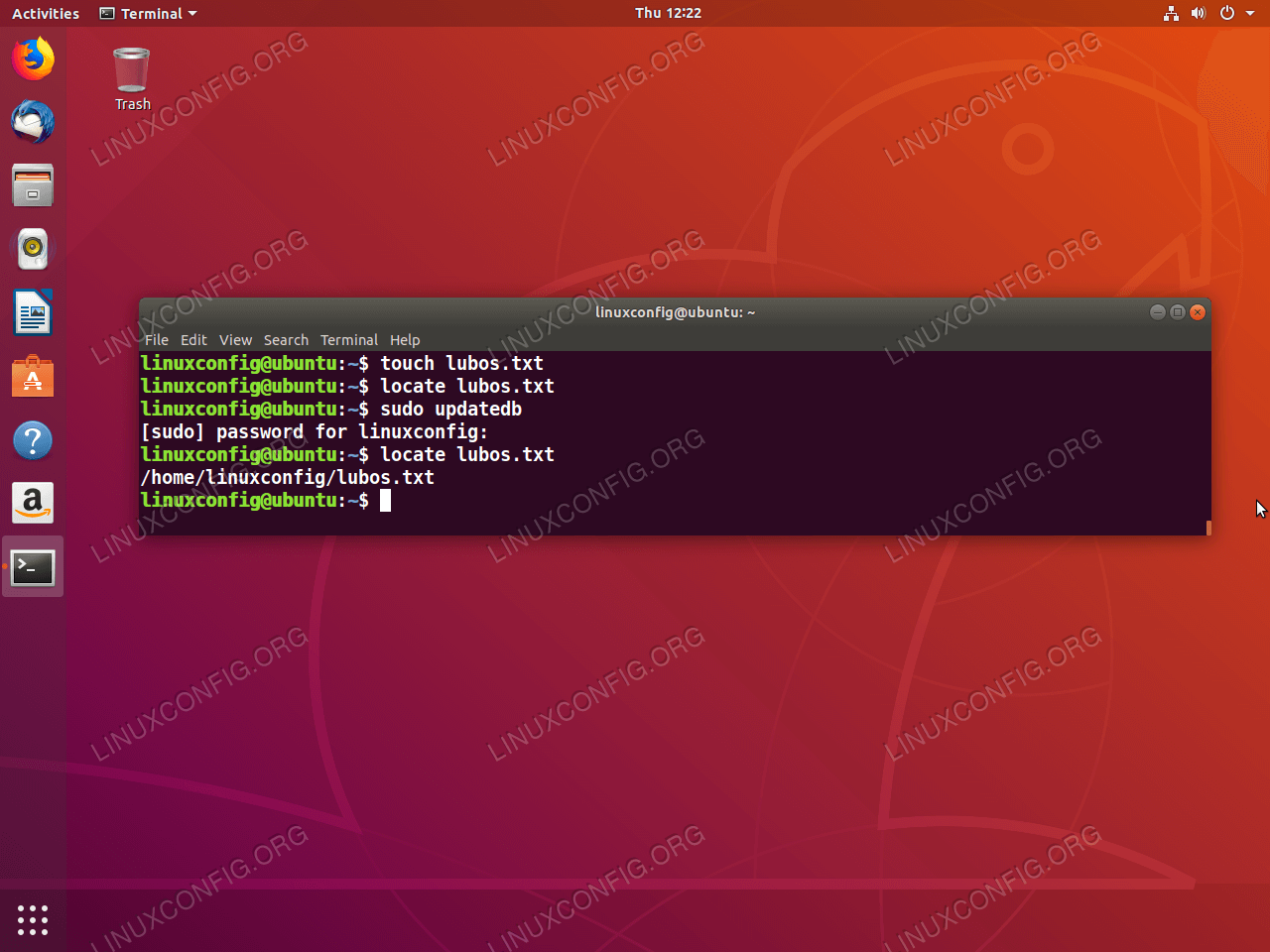
Chmod urwx,gorx filename All permission to everyone (not recommended) chmod ugorwx filename Using Octal Notation Using the octal notation you can set permissions in number between 07 Each number is calculated with the sum of read (4), write (2) and execute (1) For example, if you set permission 6, it means 42 (read write)Assign execute permission to user and group in file chmod ax ;Unix/Linux chmod command examples to Change File Permissions Also Read 40 Best Examples of Find Command in Linux Example 1 How to check chmod command version If you want to check chmod command version then you need to use chmod version command as shown below As you can see from below output current chmod version is 2
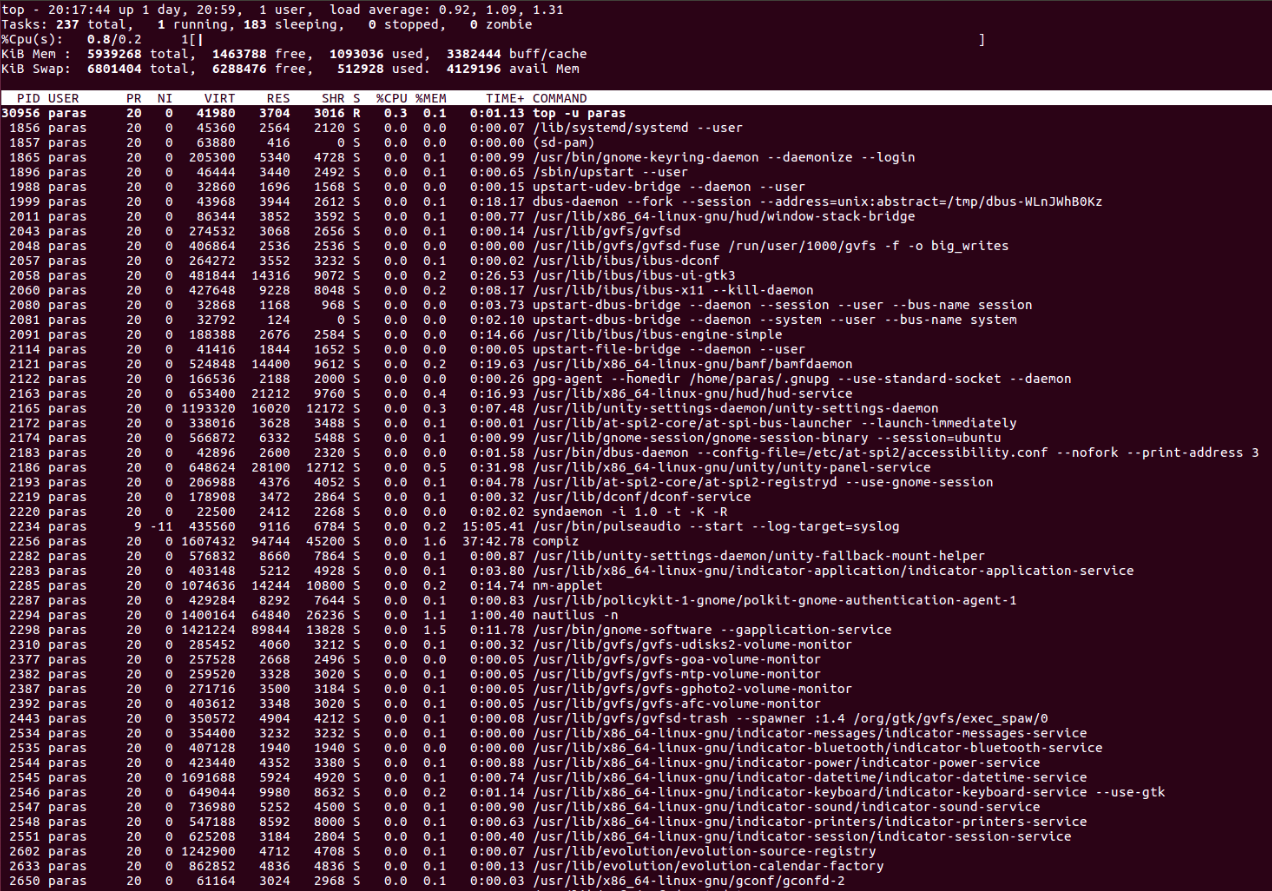


Top Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks


2 3 Basic Linux Shell Commands Bioinformatics Web Development
Chmod command in Linux is used to change or assign permissions of files and directories In Linux systems, accessibility to files and directories is specified by file ownership and permissions The chmod command in Linux stands for change mode is utilized to manage file and directory permissions Let's now dive in and examine the nature of file & directory permissions and how they can be modifiedRepulsively remove the write permission for other users chmod R ow dirnameIn this file example, sets read and write permissions for user and group $ chmod ug=rw /var/www/html/dataphp See "how to use change user rights using chomod command" for more information Conclusion We explained the chown and chmod command for Linux and Unix users
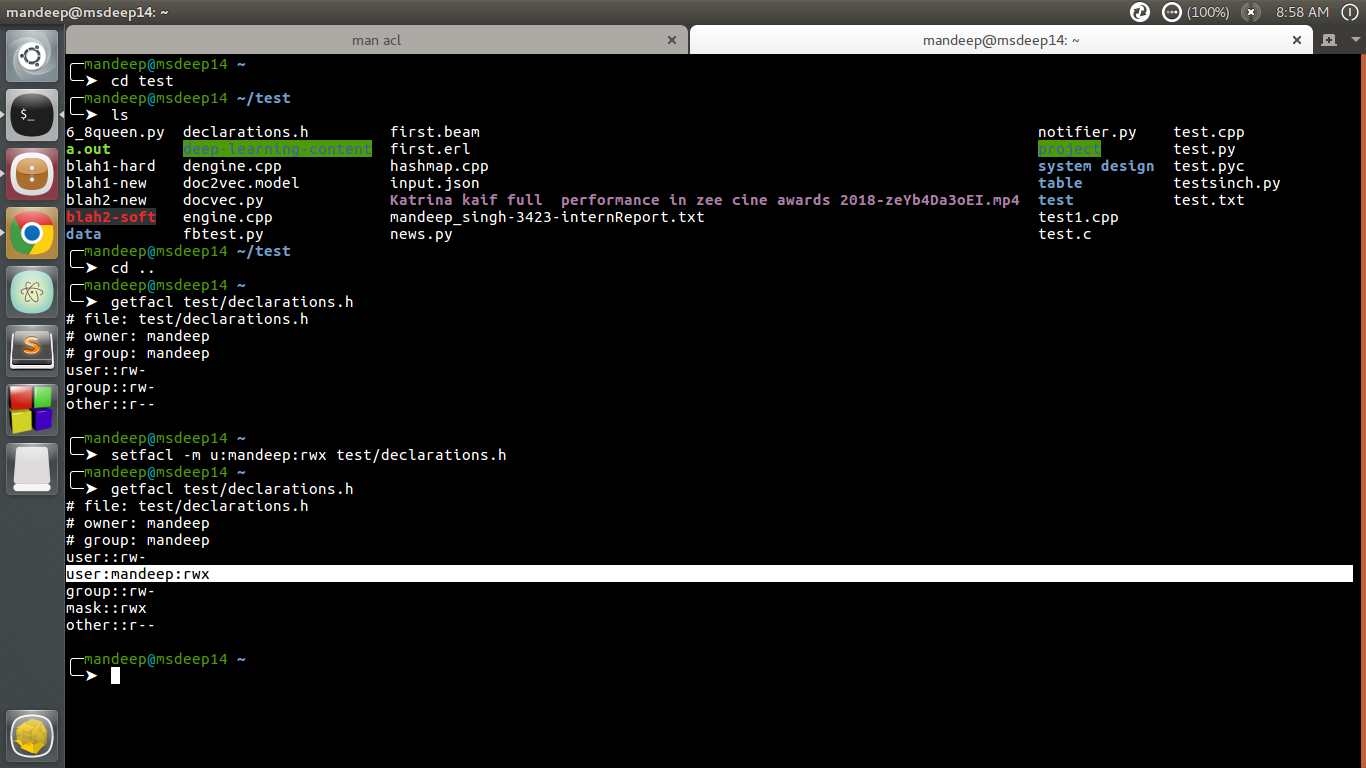


Access Control Lists Acl In Linux Geeksforgeeks



30 Linux Permissions Exercises For Sysadmins Devconnected
Chmod awx filename Example 6 Replicating user permissions to a group chmod u=g filename Example 7 Removing execute permissions to a user Chmod ux filename Example 8 Adding execute permissions to others Chmod ox Explore your self on how to use other options In the next post we will see more about chmod options and examples such as change file/folder permissions recursively, SUID, SGID and Sticky bitThe chmod command modifies the permission mode of objects in the system It is one of the most used and important commands in the set of Linux security commands A plus () symbol adds a permission, and a minus () symbol removes a permission You can read chmod ur as "user plus read," as it gives the user read permissionUse the following example to execute the chmod command in Linux Chmod {user}{add or remove permission}{permoission} Now to add permission for group users chmod grw filename To remove;



Ppt Agenda Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id


Github Fed Command Line Cheatsheet Unix Command Line Cheatsheet
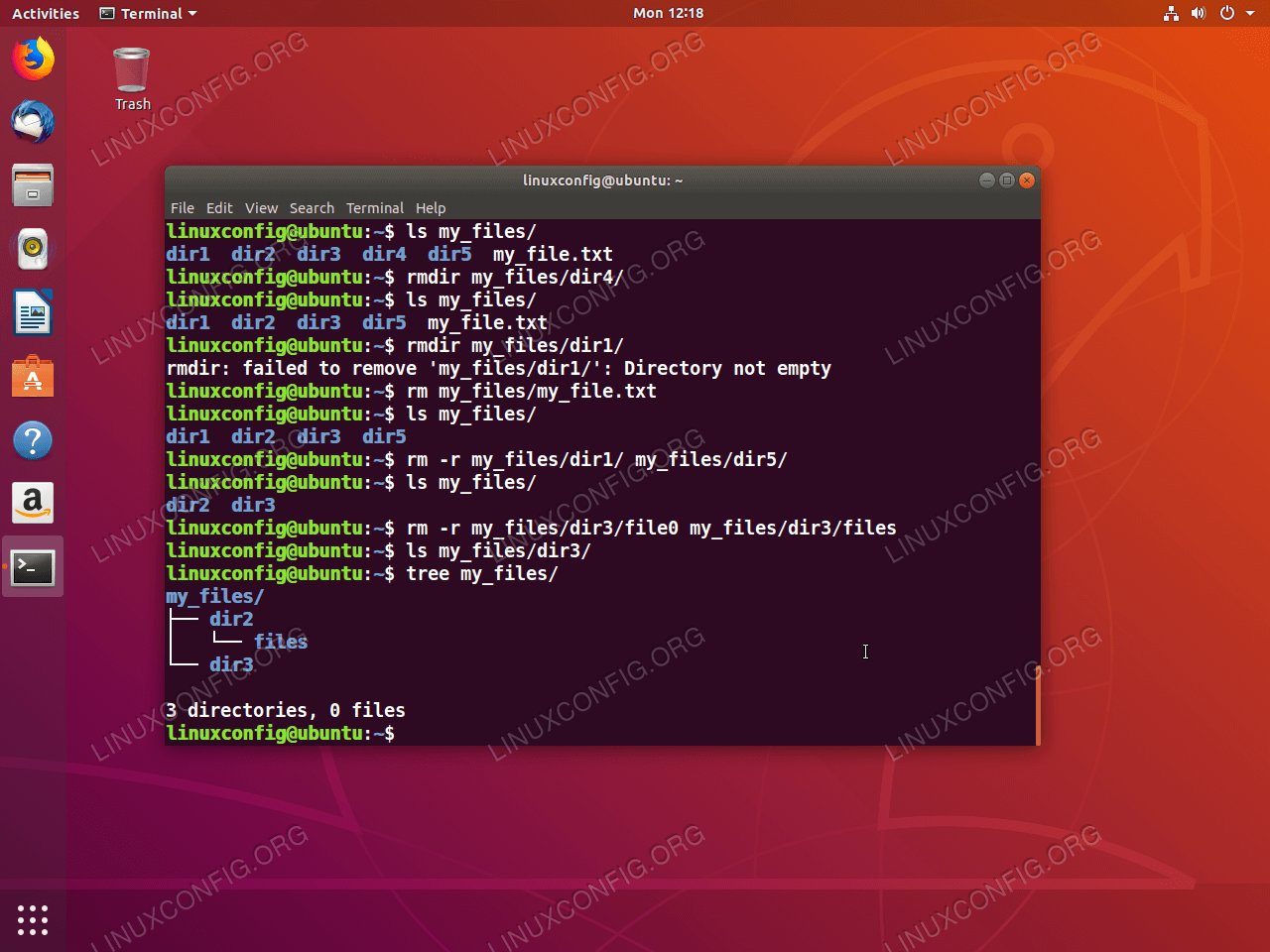
Chmod grw filename To add the given permission and remove others;A Computer Science portal for geeks It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview QuestionsIt is common to use the basic chmod command to change the permission of a single file However, you may need to modify the permission recursively for all files within a directory In such cases, the chmod recursive option (R or recursive) sets the permission for a directory (and the files it contains) The syntax for changing the file permission recursively is


50 Most Frequently Used Unix Linux Commands With Examples



Linux Permissions Making Sense Of 755 And Rwxr Xr X Serverwise
Group can read, write and executeIn this example we add permission to the user to execute pingtxt $ chmod ux pingtxt Remove File and Folder Access Permission between role and permission is used to remove permission for the given role In this example we remove users execute permission from file pingtxt $ chmod ux pingtxt Copy Permissions From Other FileChown and Chmod commands for managing file permissions in Linux system Time:5 chown Usage chown options owner group file Or chown options — Reference = reference file Change the owner and / or group of each file When using the — referenbce parameter, change the owner and group of the file to be the same as the specified reference file


The Ultimate Linux Command Line Guide Full Bash Tutorial



Top 50 Linux Commands You Must Know Journaldev
You can use chmod in the command line to change file or directory permissions on unix or unixlike systems such as linux or BSD How to use chmod?Chmodchanges the access permissions, or modes,of the specified file or directory (Modes determine who can read, write, or search a directory or file) Users with read access to SUPERUSERFILESYSCHANGEPERMS (a UNIXPRIV class profile), can use the chmodcommand to change the permission bits of any fileThe chmod command is used in Linux (and Unixlike systems) to set the permissions of files and directories First of all, here is the generic syntax of the chmod command chmod The permission part of the command can have different formats One format is a group of number like the one you see below


Basic Linux Commands Linux Cli 50 Most Used Linux Commands By Sai Kumaresh Beyondx Medium


Linux File Permissions Explained Symbolic Permissions And Chmod Part 1 Youtube
The following chmod command make changes only in all directories present inside the target directory and not on files present inside it Example user1@linuxhelp Desktop$ ll total 12 drwxrwxrx 2 user1 user1 4096 Feb 25 1445 dir1 rwrwr 1 user1 user1 21 Feb 25 1445 file1 rwrr 1 user1 user1 29 Feb 25 1446 file2 user1@linuxhelp Desktop$ chmod aX * user1@linuxhelp Desktop$ ll total 12 drwxrwxrx 2 user1 user1 4096 Feb 25 1445 dir1 rwrwr 1 user1 user1 21 Feb 25 1445We want the user dave to have read and write permissions and the group and other users to have read permissions only We can do using the following command chmod u=rw,og=r new_filetxt Using the "=" operator means we wipe out any existing permissions and then set the ones specified let's check the new permission on this file ls l new_filetxtAssign read permission to group & others in file chmod urwx ,grw,or file



Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube



An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World
Chmod command practical example Create a test file named testfile and note down its default permission Now run following commands to see how chmod command changes permission type in supplied level (as first argument) To verify the effect, use ls –l command after of each commandNow, let us see how chmod command can be used to change the access mode of a file Example 1 Let's change the assgn1_clientc permission so that the owner cannot write(w) in the file but can only read it BEFORE rwrwr mik mik assgn1_clientc COMMAND chmod u=r assgn1_clientc AFTER rrwr mik mik assgn1_clientc BeforeExtra chmod command options Verbose Changes Silent Default Recursive PreserveRoot Reference File Setuid Setgid Sticky Bit Use the octal CHMOD Command chmod R 700 folder_name OR use the symbolic CHMOD Command chmod R arwx,grwx,orwx folder_name Chmod Permissions for chmod 700 Chmod owner Owner can read;



Linux Chmod Recursive How To Change File Permissions Recursively



Bif703 File Permissions Ppt Download
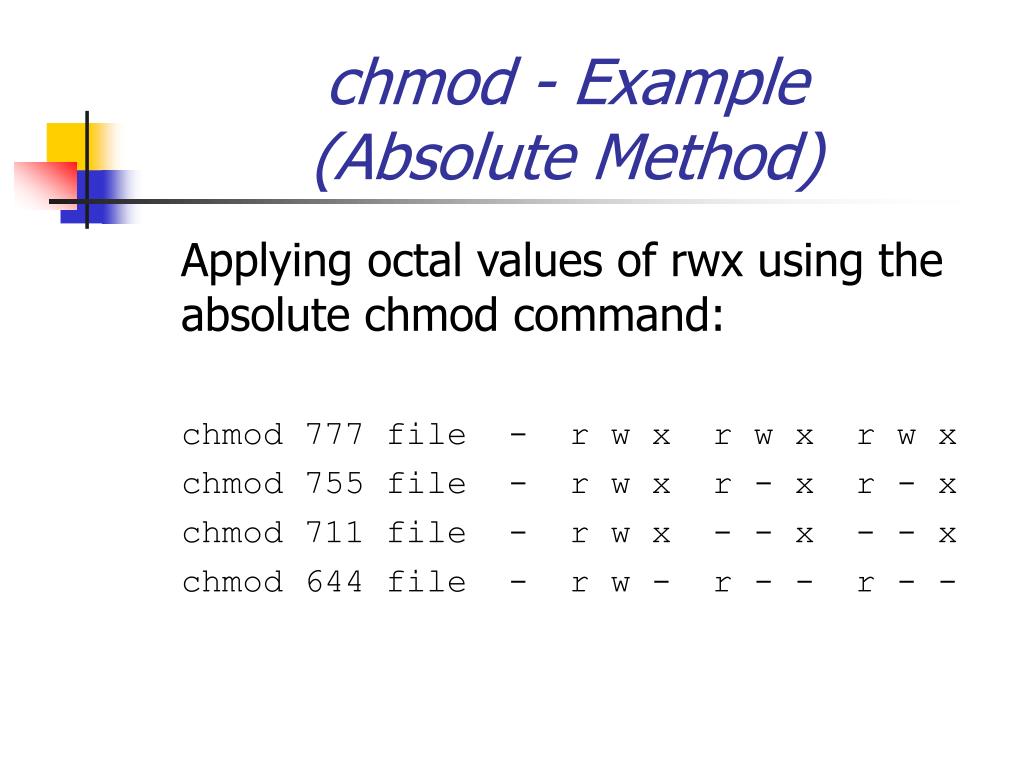
To have combination of permissions, add required numbers For example, for read and writeChmod command examples Using chmod command is very easy if you know what permissions you have to set on a file For example, if you want the owner to have all the permissions and no permissions for the group and public, you need to set the permission 700 in absolute mode chmod 700 filename You can do the same in symbolic mode chmod u=rwx filenameChmod user type(u/g/o/a) add/revoke(/) permission type(r/w/x) For instance to change permissions of the owner of a file to read and write, execute chmod urw file1txt To give write permissions to everyone, execute chmod aw file1txt To remove the write permission for all other users, we run chmod ow file1txt



How To Use The Chmod Command 2 Minute Linux Tips Network World


Chapter 10 Managing File Permissions Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 Red Hat Customer Portal
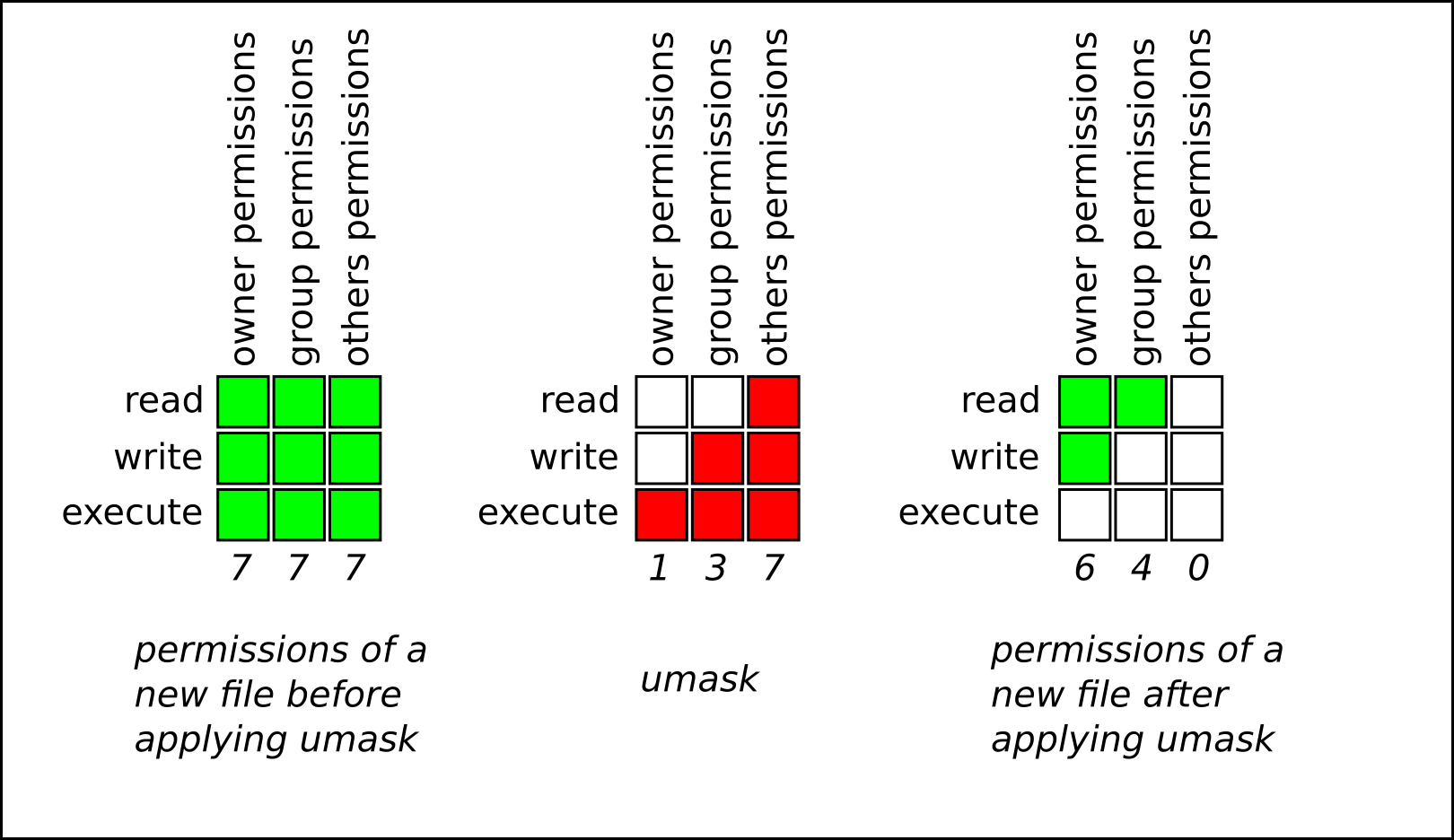
In Unix and Unixlike operating systems, chmod is the command and system call which is used to change the access permissions of file system objects (files and directories)It is also used to change special mode flags The request is filtered by the umaskThe name is an abbreviation of change mode Modes are the filesystem permissions given to "user", "group" and "others" classes to accessExample 1 Read, write, and execute for the user and group, plus only read for others, maps as localhost@user1$ chmod ugrwx,or Example 2 Read, write, and execute for the user and only read permissions for group and others maps as localhost@user1$ chmod urwx,gorChmod Examples Permissions Using Numeric mode Setting Read/Write/execute to owner Read/execute to group and everyone else to example1txt chmod 755 example1txt rxwrxrx Setting Read/Write to owner Read/execute to group and read only to everyone else to example2txt chmod 664 example2txt rwrwr–



Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Linux Line Tools Thing 1



Linux Commands With Syntax Most Commonly Used Part 4 Dataflair
We can present permissions as an octal number For example, for setting read, write & execute permissions for the owner, read & write permissions for its group, and no permission for others, to a hellotxt file, we will execute the following command sudo chmod u =rwe, g =rw,orwx hellotxtIn Linux, the chmod 644 command works for both files and directories You can set the chmod 644 commands in any Linux filesystem, server, or media player server like Plex or Emby Here is an example of how you can run the chmod 644 commands on a Linux system sudo chmod 644 /path/to/file 8 chmod 600 Allow ReadWrite, But No ExecutionYou can change file permissions in this format chmod options mode file_name You can change permissions using alphanumeric characters (arwx) or with octal numbers (777) Here's a chmod example using for setting permissions so that Owner can read, write and execute;


Some Linux Commands Cheat Sheet Linux



Proc File System In Linux Geeksforgeeks
Chmod g=x filename This is how you can use the chmod command in Linux you can also use this method to set permission for other usersThe chmod command in Linux/Unix is abbreviated as CH ange MOD e Chmod command is useful to change permission for Files and folders in Linux/Unix File/Directory permission is either Read or Write or executable for either user or group or othersTo set the permission of a file, execute a permission statement with the chmod command For example, we want to set the read and write permission for all users and groups of file 'Demotxt' We have to pass the "u=rw,go=rw Demotxt" permission statement with chmod command To display the file permission, execute the below command



Chmod X Explained Everything You Need To Know



Linux Commands An Ultimate Guide Howtodojo
Below are some examples of how to use the chmod command in symbolic mode Give the members of the group permission to read the file, but not to write and execute it chmod g=r filename;If you want to change the permission of a directory in Linux then you need to use the same chmod command what you have used in above examples for files In this example, we are having a directory example whose permission can be checked by using ls lrtd example command as shown below As you can see current permission on this directory is 0755About chmod command The chmod command is used to define or change permissioins or modes on files and limit access to only those who are allowed access It changes the mode of each FILE to MODE The chmod command stands for change mode and it's used to limit access to resources It's a same as using your mouse to rightclick a file or folder and selecting the permission tabs and



Learn Basic Linux Commands With This Downloadable Cheat Sheet Linux Cheat Sheets Cheating



Top 50 Linux Commands Command Line Interface Computer File
If you are new to Linux, and are looking for a way to change file/directory permissions through the command line, you'll be glad to know there exists a command dubbed chmod that lets you easily do this In this tutorial, we will discuss the basics of this command as well as provide examples explaining how it can be used in various scenariosChown from= currown currgroup newowner newgroup filename For example chown from=roothimanshu himanshuroot file1 The above command will check whether the existing owner is 'root' and group is 'himanshu' If yes, then owner will be changed to 'himanshu' and group will become 'root' Q5Assign execute permission to all in file chmod ox ;



How To Execute Install Sh Files In Linux Using Terminal 9 Steps



Agenda The Linux File System Chapter 4 In Text Ppt Download
The chmod command stands for change mode and it's used to limit access to resources It's a same as using your mouse to rightclick a file or folder and selecting the permission tabs and defining who can access the resource the chmod command is the way to do it on the command line



Directory How Can I Change Permissions Of A Folder Including Its Enclosed Files And Subdirectories Ask Ubuntu



Chmod Code Example



How To Use Chmod 777 Command In Linux Explained How To Use Chmod Command Hindi Tutorial Youtube



Linux Common Commands Tutorial And Use Examples Linuxcommands Site



How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples



The Chmod Command And Linux File Permissions Explained



Basic Linux Commands Linux



Learn Linux Basics Bash Command Tutorial For Beginners



How To Use Su Command In Linux With Examples Technotrending



Linux Commands Linuxconfig Org



Chmod Command Linux Page 1 Line 17qq Com



How To Use Tee Command In Linux With Examples Technotrending



Write Access Chmod Command
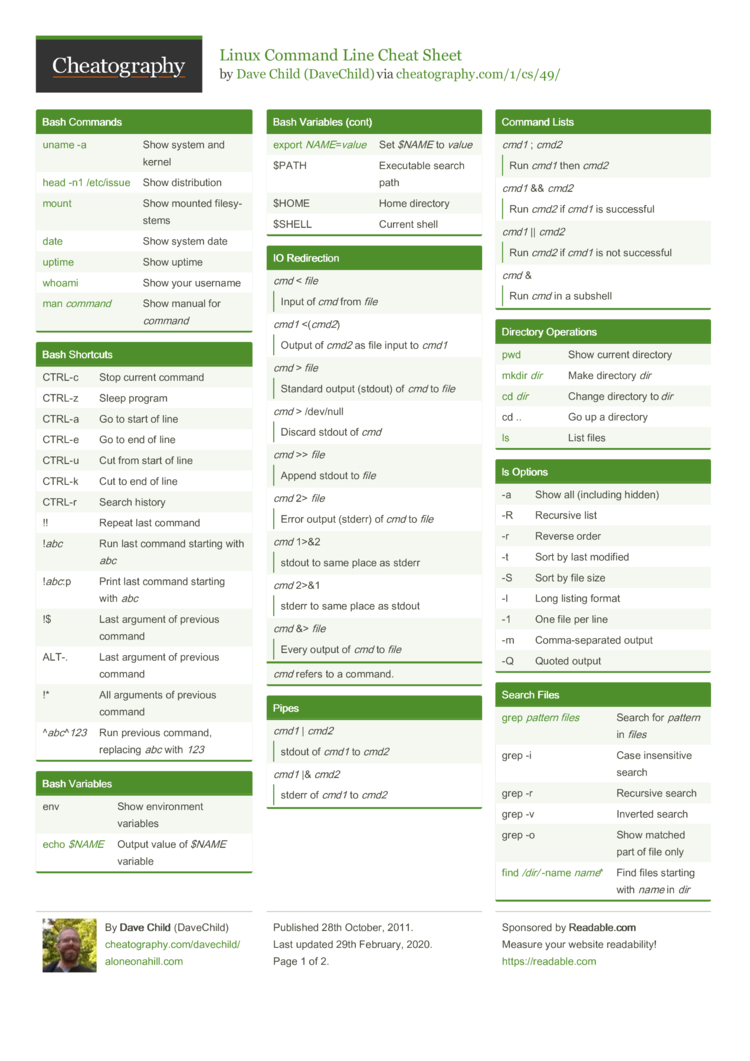


Linux Command Line Cheat Sheet By Davechild Download Free From Cheatography Cheatography Com Cheat Sheets For Every Occasion



Linux Cheat Sheet Commands Pdf Download Printable



Linux And Unix Chmod Command Tutorial And Examples Xsofthost



Hindi Linux What Is Chmod And How To Use Chmod In Linux Youtube



How To Run Unix Shell Command In Java Like Chmod Mkdir Grep Or Any Unix Commands Javaprogramto Com



Bash Sudo Abc Sh Command Not Found Ask Ubuntu



D 6 Permission Issues And How To Troubleshoot Engineering Libretexts



Unix Port Computer Networking Filename


Chmod X Windows Nativeyellow



Chmod Calculator Takes The Hassle Out Of Directory Permissions Techfruit


Chmod X Windows Nativeyellow
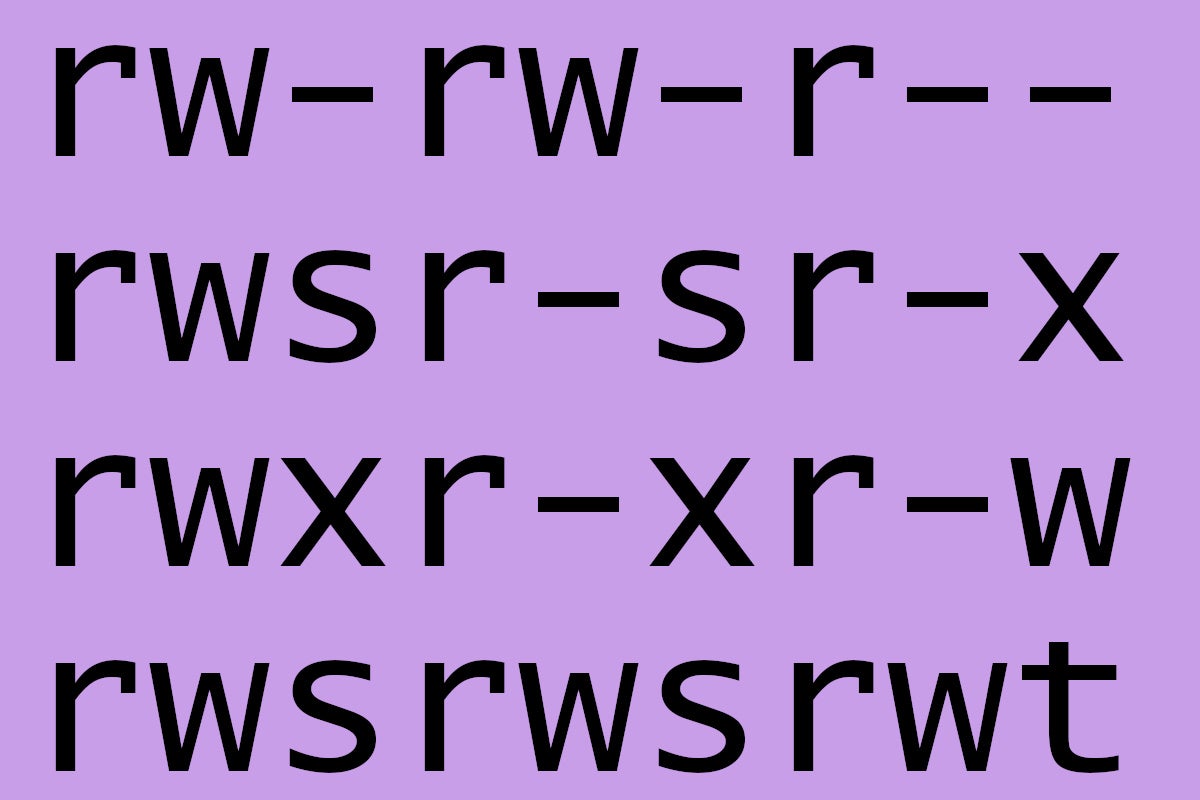


A Deeper Dive Into Linux Permissions Network World



Cp Command Tutorial In Linux Unix With Examples And Use Cases Linuxcommands Site



Change File And Folder Permission On Ubuntu Chmod Chown Command In Linux Youtube



List Of Linux Commands Every Developer Should Know



Linux Common Commands Tutorial And Use Examples Linuxcommands Site



Linux Commands Cheat Sheet Definitive List With Examples
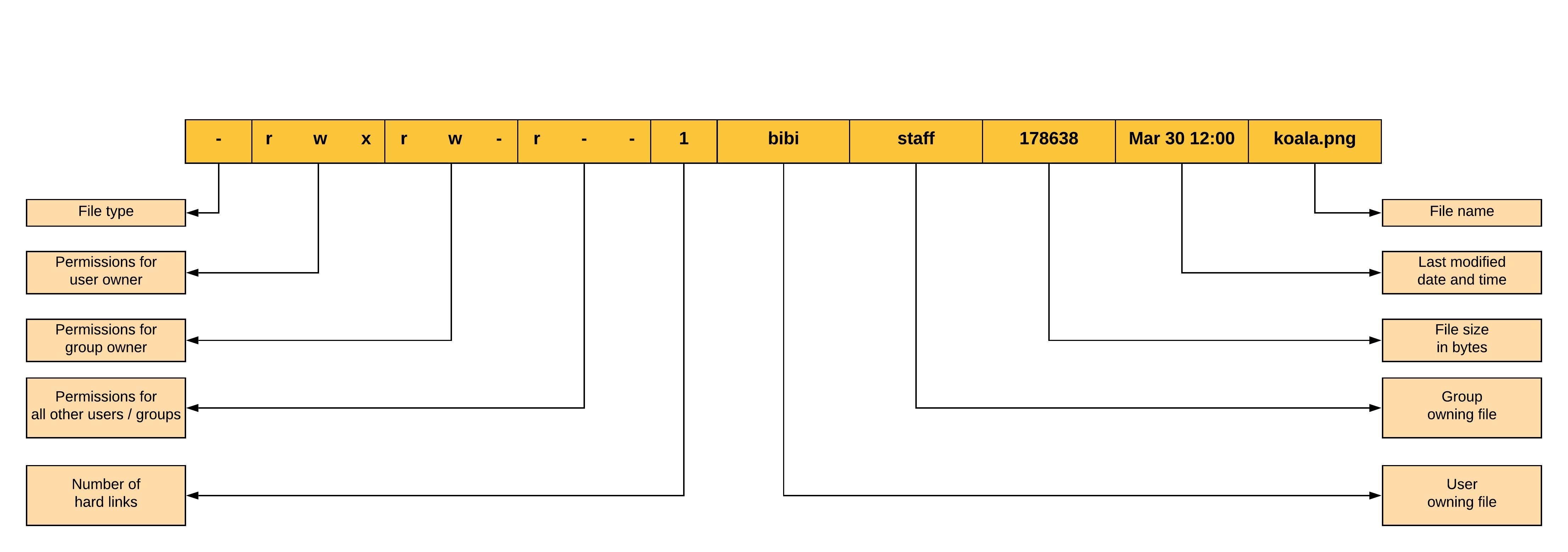


Linux File Permissions And Ownership By Udara Bibile Level Up Coding



Linux File Permission Explained In Easy Language


35 Linux Basic Commands Every User Should Know Cheat Sheet



Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier



Part 12 Unix Linux For Testers Chmod Command File Access Permissions Youtube


How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux Keepthetech



How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux The Wise Bulb



How To Set Immutable Sticky Bit With Chattr Command


Linux Commands Linuxconfig Org



The Unix Filesystem Commands



Ppt Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Powerpoint Presentation Id



Basics Of Using Chown And Chmod Commands Anto Online



Linux File Permissions Explained Learn Tech Tutorials



Some Helpful Linux Commands Recently For A Coding Challenge I Was By Kate Schlunz Medium



How To Chown Recursively On Linux Devconnected



How To Change File Permissions In Linux Skillsugar


Linux Commands Linuxconfig Org



Linux Chmod Command Summary With Examples Youtube


Ppt Agenda Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Agenda The Linux File System Chapter 4 In Text Ppt Download



Chmod 755 Command What Does It Do Codefather



How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux Technotrending
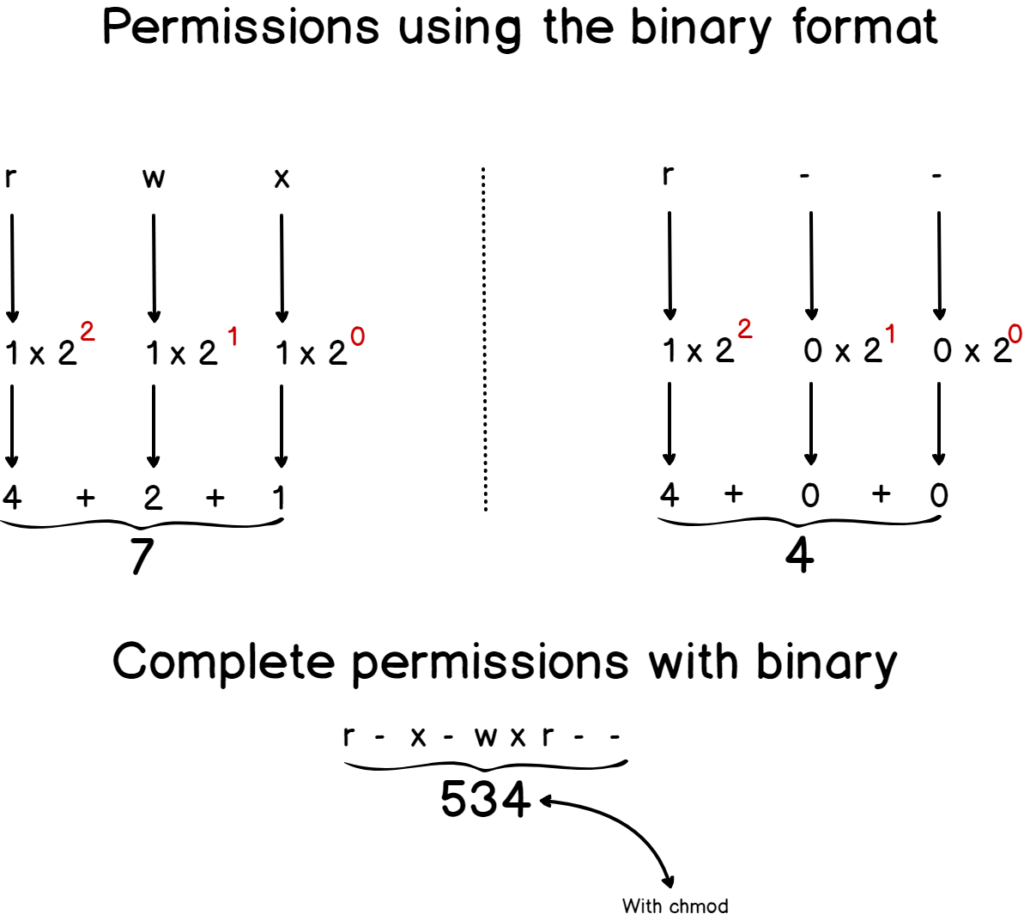


Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected



File Permissions In Linux Unix How To Read Write Change
/create-directories-linux-mkdir-command-3991847-55ea75a52f7842a2af0fdfe0b7470270.gif)


How To Create Directories In Linux With The Mkdir Command
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ls-lt-linux-command-5c4764d7c9e77c0001cb7368.png)


How To Create Directories In Linux With The Mkdir Command


Linux Commands Most Important Linux Commands Edureka


How Do Linux Permissions Work
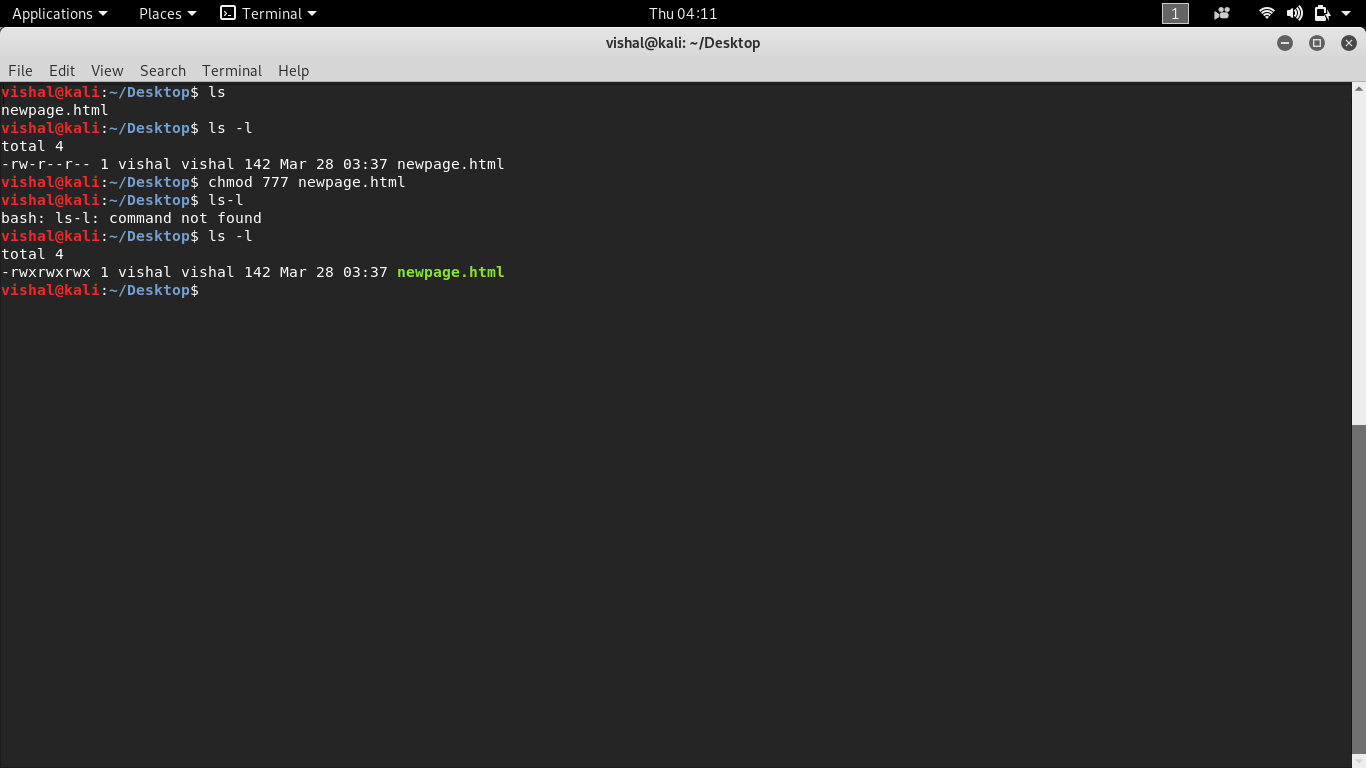


Unix Commands Basic To Advanced Unix Commands With Example



Chmod Octal Chart Zerse



How To Use Time Command In Linux With Examples Technotrending


Linux Chmod Command Utility Software Computer File



Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners



Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)


How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux



Chmod How To Set File And Directory Permission In Linux Using Chmod Youtube



10 Simple Linux Tips Which Save 50 Of My Time In The Command Line Dev Community



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿